Gout is a painful condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and while its symptoms can be managed with proper treatment, it’s important to understand the role that genetics can play in its development.
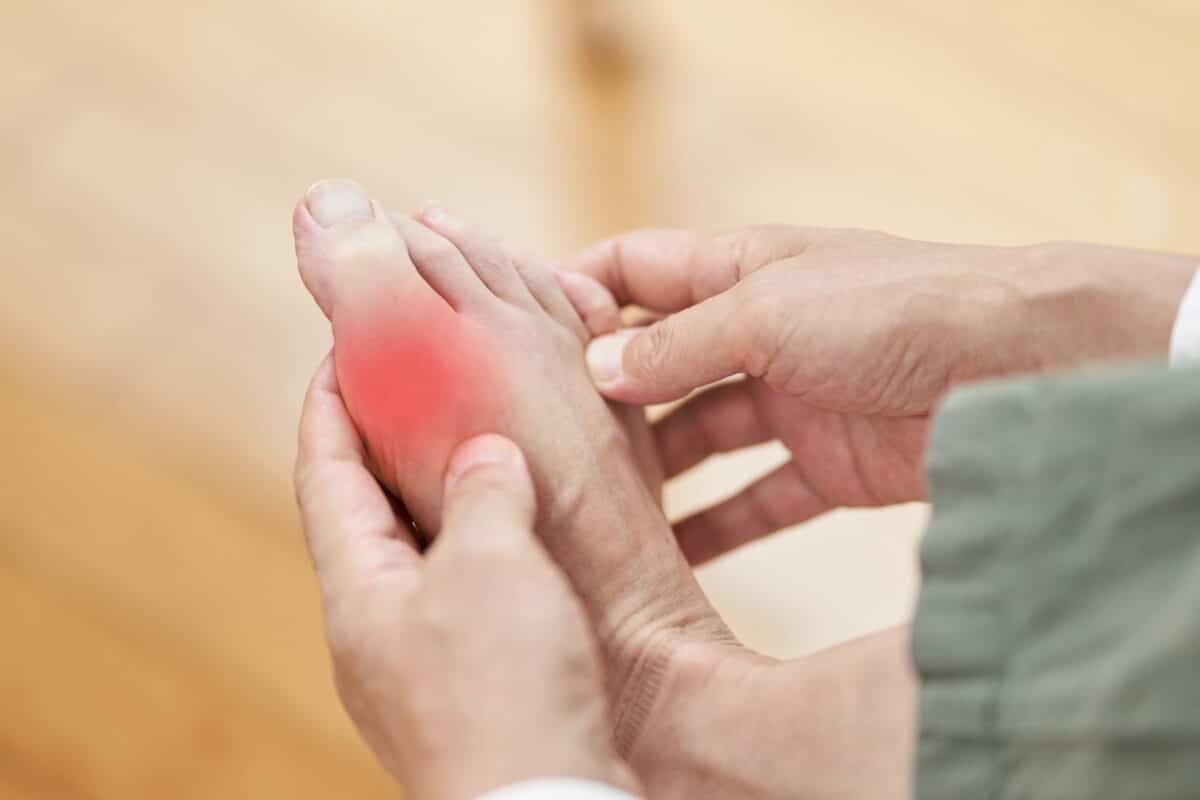
If you have a family history of gout, you may be at a higher risk of developing this condition. Gout is caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood, which can lead to the formation of crystals in the joints, causing inflammation and pain. While lifestyle factors like diet and alcohol consumption can also contribute to high uric acid levels, genetics can play a significant role.
Studies have shown that gout tends to run in families, and individuals with a family history of gout are more likely to develop the condition themselves. This is because certain genes can affect the way that the body processes and eliminates uric acid, making some people more susceptible to its build-up in the blood.
In fact, research has identified several genes that are associated with gout, including SLC2A9, ABCG2, and SLC22A11. These genes are involved in the transport and elimination of uric acid, and variations in these genes can increase an individual’s risk of developing gout.
However, having a genetic predisposition to gout does not necessarily mean that you will develop the condition. Lifestyle factors like diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption can also play a role, and making healthy choices can help reduce your risk.
If you have a family history of gout, it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms of the condition, such as sudden and severe joint pain, redness, and swelling. Early diagnosis and treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Gout is a complex condition with both genetic and lifestyle factors contributing to its development. While genetics can increase your risk, making healthy lifestyle choices can help reduce that risk and manage symptoms if you do develop the condition. If you have a family history of gout, talk to your healthcare provider about steps you can take to stay healthy and manage your risk.