Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary Tract Infections
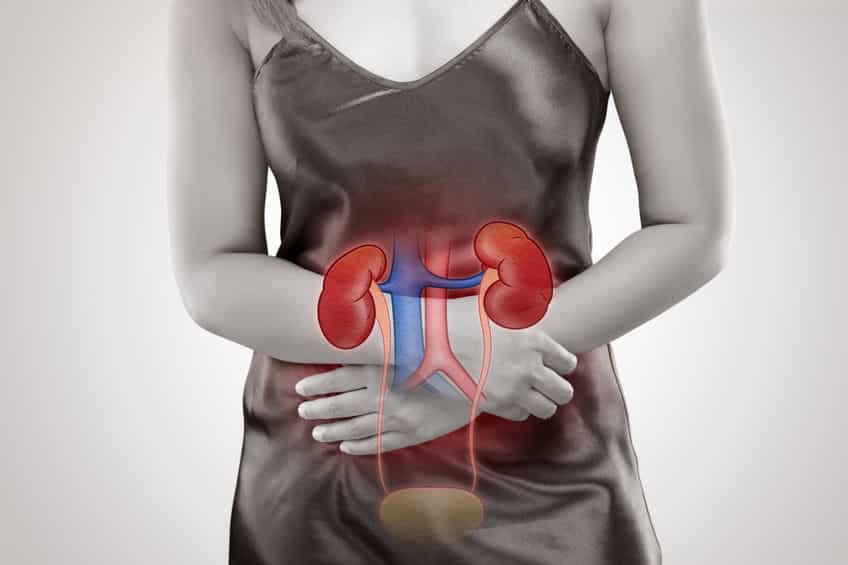
A urinary tract infection, commonly known as a UTI, is a bacterial infection that affects the urinary tract. While UTIs can occur in various parts of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, or urethra, most cases involve the bladder or urethra (lower tract).
It is essential to address UTIs promptly as they can lead to serious conditions or complications if left untreated. Among women, approximately 20 percent experience a UTI at some point in their lives.
Neglecting UTIs can result in complications like sepsis, permanent kidney damage, and an increased risk of preterm birth and low birth weight babies. Additionally, recurrent infections may become a concern.
Causes of urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection can develop when bacteria enters the urethra and starts to multiply in the bladder.
• Sex
• Constipation
• Uncontrolled diabetes
• Not urinating when you have to go (holding it)
• Dehydration
• Birth control
• Feminine products
• Kidney stones
Risk factors of urinary tract infections

Risk factors of urinary tract infections
Women are more likely to develop UTIs than men. Risk factors for women include:
- Length of the urethra in a woman — women have shorter urethras than men, so bacteria do not have to go as far to get to the bladder
- Being sexually active
- Using diaphragms or spermicidal agents for birth control
- Going through menopause – after menopause, women are more vulnerable to infection
Risk factors for men and women include:
- Blockages in the urinary tract caused by kidney stones or an enlarged prostate
- Chronic diseases, such as diabetes, that suppress the immune system
- Use of catheters
- Abnormalities in the urinary track
Symptoms of urinary tract infections
Symptoms of UTIs depend on if it is located in the upper tract (kidneys or ureters) or lower tract (bladder or urethra).
Lower tract UTI symptoms include:
- Rectal pain in men
- Pelvic pain in women
- Burning during urination
- Increased frequency of urination
- Bloody or cloudy urine
Upper tract UTI symptoms include:
- Pain in the upper back or sides of the body
- Fever or chills
- Nausea or vomiting
- Diagnosis of a urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection can typically be diagnosed in a urine test during a visit with your doctor.
- Treatment for urinary tract infection
The treatment for a urinary tract infection depends on the underlying cause of the infection. If bacteria are responsible for the infection, antibiotics will be prescribed. Oral antibiotics are effective for treating lower urinary tract infections, whereas IV antibiotics are necessary for upper urinary tract infections.
For individuals experiencing recurrent urinary tract infections, the treatment approach may involve long-term, low-dose antibiotics or a single antibiotic dose after sexual intercourse, especially if the infections are related to sexual activity.
To address concerns about antibiotic-resistant bacteria, researchers are exploring alternative treatments to antibiotics. In the case of a UTI caused by a virus, antiviral medication may be prescribed, and for UTIs caused by fungi, antifungal medication may be administered.
- Recovery from urinary tract infections
Most uncomplicated UTIs can be effectively treated with antibiotics. For women, a three-day course of antibiotics is commonly prescribed, while men may require a longer treatment period of seven to fourteen days.